What is Zero Trust?
Zero Trust Architecture is a cybersecurity framework that challenges the traditional approach of granting trust based on network location. In a Zero Trust model, all users, whether inside or outside the organisation’s network, are required to undergo authentication, authorization, and continuous validation of their security configuration before being granted access to applications and data.
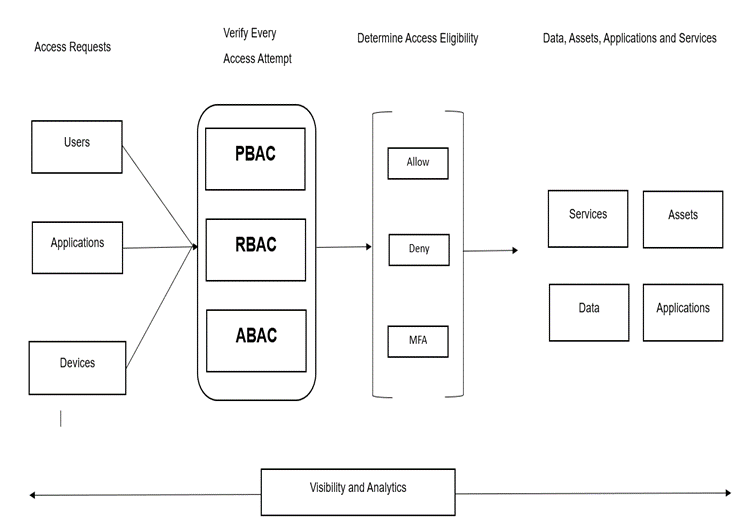
The fundamental principle of Zero Trust is that no user or application should be trusted by default. Instead, access is granted based on adhering to Zero Trust principles and undergoing policy checks at every step. This approach aims to minimise the potential attack surface and mitigate the risk of unauthorised access.
Why is Zero Trust important?
The rapid advancements in networking and cloud computing have led to complex enterprise architectures with multiple security layers. These layers include network segmentation, application security, cloud security, and container security. As a result, it has become challenging for IT teams to provide secure and instant access to resources for both on-premises and remote employees.
Traditional methods, such as Virtual Private Networks (VPNs), have been the primary means of providing remote access. However, VPNs are not foolproof as they provide unlimited access to a
network once users are authenticated. This makes them vulnerable to attackers who can exploit this access to perform lateral movement, privilege escalation, and dwell within the network for extended periods.
Zero Trust Architecture offers a solution to these challenges. By blocking attackers, both inside and outside the network, providing centralized, management of security policies, enabling service segmentation, and enhancing visibility and auditing, Zero Trust provides a comprehensive approach to cybersecurity.
Major Components of Zero Trust Architecture
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) : Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) is a critical component of the Zero Trust model. It utilises identity-based authentication to establish trust and grants access to authorised entities while concealing information about physical networks, such as IP addresses. ZTNA offers centralized management and flexibility for IT and security teams, allowing them to grant access to specific applications or data based on factors such as the current time, user location, device, and other criteria.
Multi-factor Authentication (MFA) : Multi-factor Authentication (MFA) is an essential security measure that verifies user identity through multiple methods before granting access. These methods can include security questions, email verification, text messages, biometric ID checks, and more. Implementing MFA at every access point, both for inbound and internal network traffic, forms the foundation of Zero Trust
Micro-segmentation : Micro-segmentation involves dividing networks into logical units and applying policies to control access to data and applications within these segments. By segmenting the network and restricting traffic between segments, organisations can significantly enhance security. This approach is applicable to both on-premises data centres and cloud environments, and it allows security teams to determine how applications share data, define data transfer boundaries, and enforce authentication measures for specific interactions.
Identity and Access Management (IAM) : Identity and Access Management (IAM) is a security framework that enables organisations to manage digital identities effectively. IAM empowers administrators to control user access to sensitive information within their organisations by securely storing identity and profile data. IAM supports mechanisms like Single Sign-On (SSO), Multi-factor Authentication (MFA), and Privileged Access Management (PAM), ensuring that users only gain access to applications and data necessary for their roles.
Implementation of Zero Trust Solution
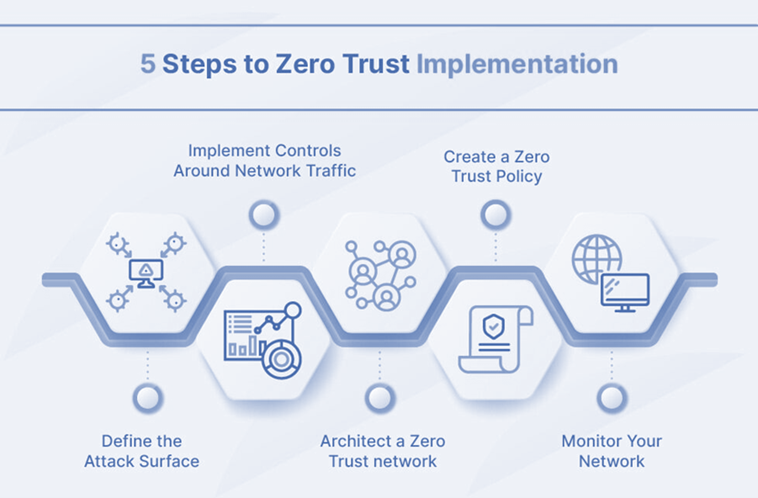
Implementing a Zero Trust framework requires careful planning and execution. Consider the following steps to deploy a Zero Trust solution effectively:
- Define the Attack Surface : Before implementing Zero Trust, it is crucial to identify and prioritize the areas that require protection. By focusing on the most valuable digital assets, such as sensitive data, critical applications, and physical assets, organizations can avoid being overwhelmed with policy implementation and tool deployment across their entire network.
- Implement Controls Around Network Traffic : Understanding the dependencies and flow of network traffic is essential for implementing effective network controls. By analyzing the specific details of how traffic flows through the network, organizations can determine which controls to implement and where to position them. This ensures that requests are routed securely and that sensitive information and architecture are adequately protected.
- Architect a Zero Trust Network : Designing a Zero Trust network requires tailoring the architecture to the organization’s specific needs. While there is no one-size-fits-all solution, a typical approach involves starting with a next-generation firewall (NGFW) to segment areas of the network. Additionally, implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) ensures thorough user vetting before granting access.
- Create a Zero Trust Policy : After architecting the network, organizations should design their Zero Trust policies. The Kipling Method, which involves asking who, what, when, where, why, and how for every user, device, and network seeking access, can help in defining these policies effectively. By considering these factors, organizations can establish granular access controls that align with the principles of Zero Trust.
- Monitoring : Monitoring network activity is crucial for identifying potential security issues and optimizing network performance. By implementing robust monitoring solutions, organizations can proactively detect and respond to threats, ensuring continuous security and operational efficiency.
How can SecurDI help?
SecurDI is a trusted provider of comprehensive security solutions, boasting over 60+ years of combined experience in securing digital transformation. Their range of services includes security assessments, deploying solutions to address vulnerabilities, and operating those solutions to improve cyber security posture. SecurDI works closely with clients to understand their specific security requirements and develops tailored solutions to meet those needs. By partnering with SecurDI, organizations can enhance their security defenses and protect themselves from evolving cyber threats.

